In April 2023, the Department of Analytics and Marketing Research of TELS GLOBAL prepared the Marketing Audit of Global and Local Markets for the Board of Directors to adjust the development strategy taking into account existing trends, risks, and forecasts. In the document, social and political, geoeconomic, and economic factors are assessed according to their significance, as well as the most expected scenarios for the development of different regions and forecasts are presented.
The content of the document body is given below.
SUMMARY
The document is preceded by a summary section, which presents the conclusions of the entire research.
Conclusion on Expediency of Reviewing the Corporate Strategy
It is not necessary to review the Corporate Strategy, as all changes now take place at the detail level, without overriding the detected trends at a high level, which were announced earlier when formulating the Corporate Strategy. However, it is better to be ready for tactical corrections:
- The market in Europe will operate on a declining economic background: all major European economies are expected to be low at growth. The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is lower than the neutral ones for many months now. The number of production orders declines because of inflation (precisely for Poland and Germany, according to the Polish mass media). It means decrease of cargo base and increased competition for cargo.
- In case the situation in Taiwan develops into a military conflict with China, Europe will have to choose a side to support during the conflict. It is obvious that China will not be favorite here, although it will be traumatic for European economy. The reaction can be seen in sanctions as the Russian ones. The risk of such a turn of events is high, but still not fatal, as it may not come to a military confrontation.
Social and Political Factors
Fundamental trends in social and political sphere have been preserved and are gradually developing:
- partition of the global market to regions continues;
- political confrontation between Russia and the Western Coalition keeps growing;
- tension between the USA and China increases;
- protest social activity in Europe is going up.
There is a parallel escalation between Russia and the West and between the USA and China. China is forced to get closer with Russia. These countries will never become the united camp, but can and are becoming situational allies.
The gradual escalation between the East and the West is likely to continue, with some aggravation in the second quarter, and come out to a possible “truce” in the third quarter, but not with a resolution of a significant difference. Now all sides have enough resources and volition to get their victory, but they fear taking steps to severe exacerbation.
Protest activity keeps growing in Europe. Trade unions are holding strikes to raise salaries, industry associations are demanding that governments take action to protect the interests of enterprises in their industries. At the moment, it is highly seen in transportation, oil refining, and agriculture.
Geopolitical and Geoeconomic Factors
The priorities have changed in trade and logistics. Now supply chains are lined around the countries that are thought to be political and economic allies. The following trends are observed in the management of economic entities:
- increasing attraction to domestic resources (development of domestic market by means of reducing foreign economic activity);
- geoeconomic fragmentation – abandonment of global economic integration;
- fragmentation of capital flow along geopolitical fractures and potential creation of regional geopolitical blocks;
- increase in geopolitical risks and interest of companies in “reshoring” and “friend-shoring”.
Explanation: “reshoring” is a process of returning production back to the original country, which was previously relocated to lower-cost countries; “friend-shoring” is redirection of supply chains to the countries that are considered to be politically and economically safe or with a low risk level which makes it possible to avoid failures when organizing logistics.
Economic Factors
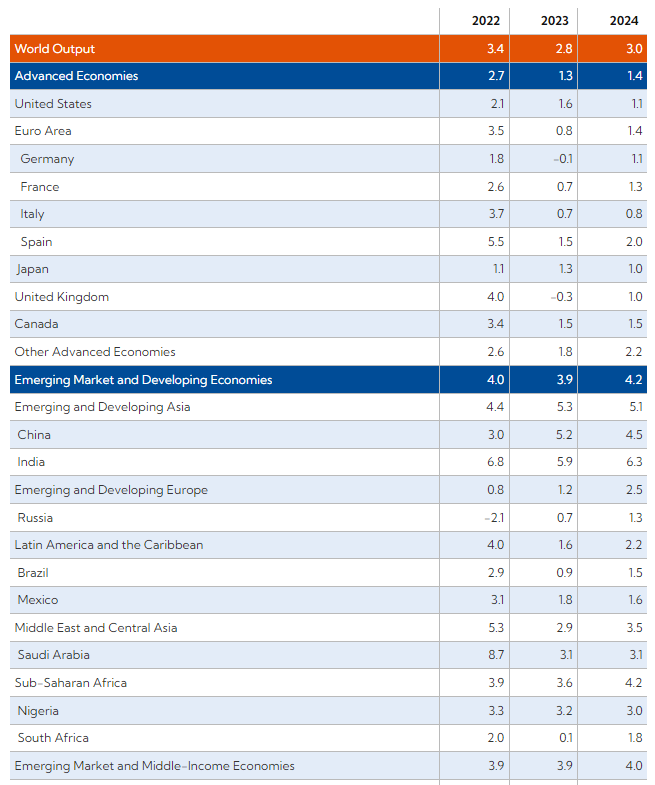
The IMF has improved its forecast of economic growth for 2023:
- growth of the global economy – from 2.7% (forecast dated October 2022) to 2.8% (forecast dated April 2023);
- developed economies – from 1.1% (October 2022) to 1.3% (April 2023);
- emerging and developing economies – from 3.7% (October 2022) to 3.9% (April 2023)
- Euro area – from 0.5% (October 2022) to 0.8% (April 2023)
- emerging and developing economies in Asia – from 4.9% (October 2022) to 5.3% (April 2023).
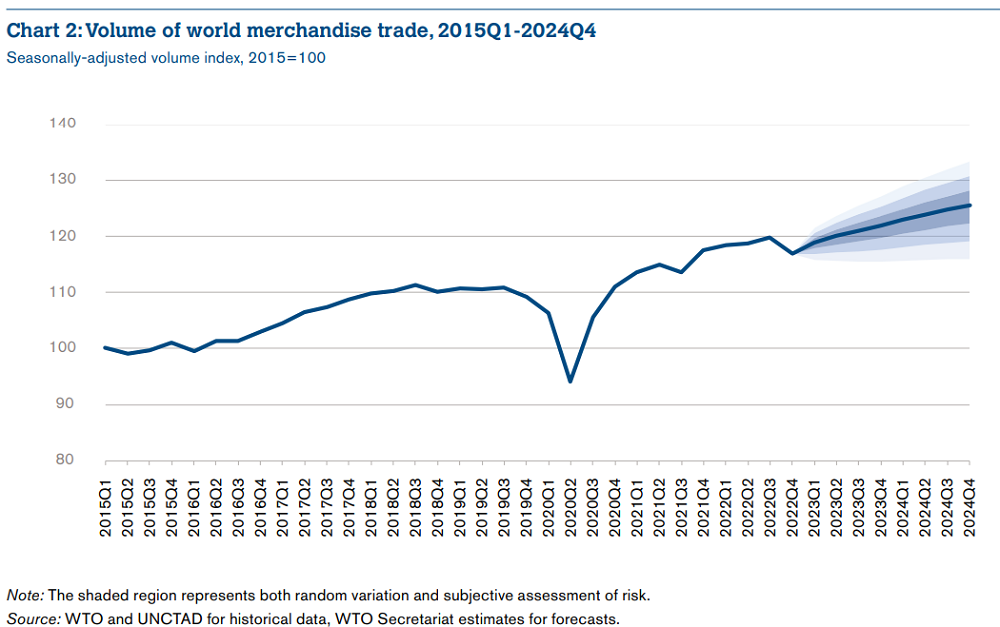
At the moment, the WTO forecasts growth of goods trade volume by 1.7% in 2023 (in October 2022, the growth was expected to be by 1.0%). Still the rate of expansion of global trade in 2023 is expected to be lower than in previous years.
It is expected that foreign trade in China (import and export) and export from the Russian Federation will be lower. Europe will face decrease in import.
Now let's focus on every factor group in detail
Social and Political Factors
The feature of this crisis and its difference from the previous ones: it is not intrasystem (when subjects solve problems within the current rules and laws), it is the crises of the world relation system itself (laws are not followed, and the relation system is to be reviewed or reestablished). Such crises are very difficult to forecast, as there are a lot of variants of how events may develop. And when a crises includes military components with a prospect of escalation it is practically impossible to forecast things more or less accurately, making this process more like fortune telling.
Fundamental trends in social and political sphere have been preserved and are gradually developing:
- partition of the global market to regions continues;
- political confrontation between Russia and the Western Coalition (with the hot spots in Ukraine) increases;
- tension between the USA and China increases;
- protest social activity in Europe is going up.
Europe
Thanks to the accumulated economic potential Europe is holding strong during this current complicated situation. The economic problems it faces today are connected primarily with sharp increase in energy sources, which boosts inflation.
However, pessimistic sentiments are tend to grow. In particular, the PMI for the industrial sector of Poland for the eleventh month in a row is lower than the neutral level of 50 points. The PMI in Germany fell very low (44.7 points). In average, in March the PMI fell to 47.4 points in the Euro area. The forecasts of analytical centers regularly lower the expected growth rates.
Protest activity among the population keeps growing in Europe. Trade unions are holding strikes to raise salaries, industry associations are demanding that actions should be taken to protect the interests of enterprises in their industries. At the moment, it is highly seen in transportation, oil refining, and agriculture.
Still there are not evident signs that the general political course of Europe can be changed or there will be a split within the European Union, as the current political elites are influential enough to keep the situation under control.
Europe accelerated the process of transition to “green” energy, the share of this energy is growing, however it can be associated with decrease in consumption of carbon energy resources.
European business obviously takes interest in developing economic relations with China, but they have risks due to a possible military conflict between China and the USA and their allies because of Taiwan that can force Europe “to choose a side”.
The active position of Poland in the Russian-Ukrainian conflict for the last month increased the risk of its direct participation in the war. There are many indications that a Polish-Ukrainian political union is emerging. This is a state union on certain terms. A lot will depend on the results of exacerbation of military actions in Ukraine in spring and summer. If the results are not in favor of Ukraine, then the risks of Poland participation in the war will increase even more.
China
The current year became critical for China. The original idea of the Silk Road (which was aimed primarily at the sales market in Europe) has been in a great danger since last year for a number of reasons. If the situation develops negatively, the European market can be significantly reduced for China.
In its desire to compensate for the risks, China keeps actively developing the domestic market of industrial and consumer demand, but it is still a long way to the level of Europe. Other continental sales markets are not as receptive as the European one, but the PRC tries to develop everywhere, where any prospect can be found.
On the one hand, the conflict between Russia and the West creates favorable conditions for China to import cheap Russian energy resources. However it means acquisition and dependency on Russia, and that is what China tries to avoid with the help of supply diversification.
Militarization in China is in full swing – both at the social and ideological level and in the real military sector. It is seen even in such examples as equipping of civilian cargo ships (in particular, COSCO) for rapid “conversion” into landing craft. The country is getting ready to a possible military conversation with the USA and its allies (Australia, Japan, etc.).
The behavior of China is driven by the facts of Western arms shipments to Taiwan and announcement of the USA officials on possible direct participation of the USA military forces in case of the forcible takeover of Taiwan by China. Because of the development of this conflict, the risks of increasing sanctions restrictions, as well as military threats, China is forced to get closer with Russia.
In order to strengthen allied relations with the Russian Federation, China officially voiced a neutral position on the Kuril Islands (previously it supported Japan's claim) for the first time since 1964.
For the first quarter of 2023, foreign trade between China and the USA significantly reduced (-13%), and with the Russian Federation significantly increased (+39%).
The political influence of China is growing in the Middle East. Through its mediation, Saudi Arabia and Iran have reestablished diplomatic relations, which were severed seven years ago (the countries make up the orbit of the Silk Road). In fact, this was the first case of China's behavior as a major influential political player in the region. And here it acted as a political competitor of the USA in the matter of influence on Saudi Arabia. (As a reminder, Saudi Arabia decided to reduce oil production against the interests and direct wishes of the United States).
Türkiye
Despite the difficult economic backdrop (high inflation, problems after the earthquake), Türkiye is increasing its role as a logistics hub for all kinds of goods (energy or consumer ones). Meanwhile, Türkiye has a sufficiently wide range of its own goods to conduct active foreign trade.
Türkiye is determined to have stable, peaceful relations with all major players. It skillfully balances on the edge of peaceful coexistence with Russia and protection of its interests in the Middle East (the main contradictions are over Syria). Russia is seen as an important goods donor for the role of an energy hub, and also as a sales market for its goods.
A lot will depend on the next presidential election in Türkiye. If Erdoğan stays, the country will follow the same course. The other candidate may become more of a spokesman for Western interests, with all the consequences that this implies.
Russian Federation
The economy of Russia has showed high resistance to the sanction shock wave. However, in the midterm run the sanctions will put pressure on economic growth. Many financial analysts have increased forecasts on the Russian GDP for 2023, but with forecasts for 2024 being lower.
Russia has diversified exports of oil and petroleum products or found bypass mechanisms for supplying the same consumers. The military situation significantly supported the GDP by means of defense orders. Now not only the military enterprises are busy with orders, but also the related ones (sewing, chemical, etc.). The government has poured considerable money into the economy from the funds it previously accumulated. Since last November, the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) in the production sphere has held steady above the neutral 50 points.
The political system of the Russian Federation is now stable. Financial contributions to the economy keep coming. At the same time, Russia experiences personnel shortage in almost all spheres. The mass departure of specialists abroad last year contributed to this to a large extent.
Not only political but also military cooperation with China is quickly strengthening, which can be seen in the increasing frequency of contacts between military departments.
Geopolitical and Geoeconomic Factors
Global trade is one of the most important components of the global GDP (according to the latest data, it constitutes 57% of the global GDP). Because of the disturbances of the last 2 years, the foundation of global trade – the supply chain system – has broken down. Emerging deglobalization exacerbates the problem of supply disruption. The priorities have changed in trade and logistics. Now supply chains are lined around the countries that are thought to be political and economic allies.
Among the solid trends, there are:
- the growing priority of domestic economic policy (development of domestic resources);
- geoeconomic fragmentation – reverse of global economic integration;
- fragmentation of capital flow along geopolitical fractures and potential creation of regional geopolitical blocks;
- increase in geopolitical risks and interest of companies in “reshoring” and “friend-shoring”.
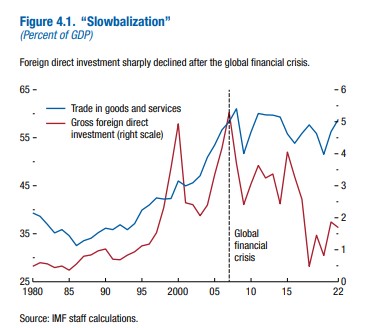 Reduction of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) After the Global Financial Crisis
Reduction of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) After the Global Financial Crisis
The slowdown in globalization, often referred to as “slowbalization”, was a consequence of the global financial crisis. Global FDI declined from 3.3% of the GDP in the 2000s to 1.3% between 2018 and 2022.
The fragmentation of capital flows due to geopolitical splits and the potential emergence of regional geopolitical blocks are new elements that could have serious negative consequences for the global economy.
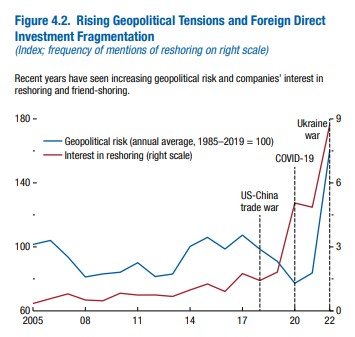
Increasing Geopolitical Tensions and Fragmentation of Foreign Direct Investment
The renewed protectionism has limited trade. Political resistance to immigration slows the labor flow. National security concerns impede the flow of technology and data. Global integration is being replaced by “reshoring” and “friend-shoring” stimulated by rising political tensions between countries.
More and more companies are turning their attention to countries with aligned political preferences to make supply chains less vulnerable to geopolitical tensions.
Economic Factors
In March this year, the IMF improved its forecasts of global economic growth for 2023–2024 compared to its forecasts dated October 2022. Now the Fund expects:
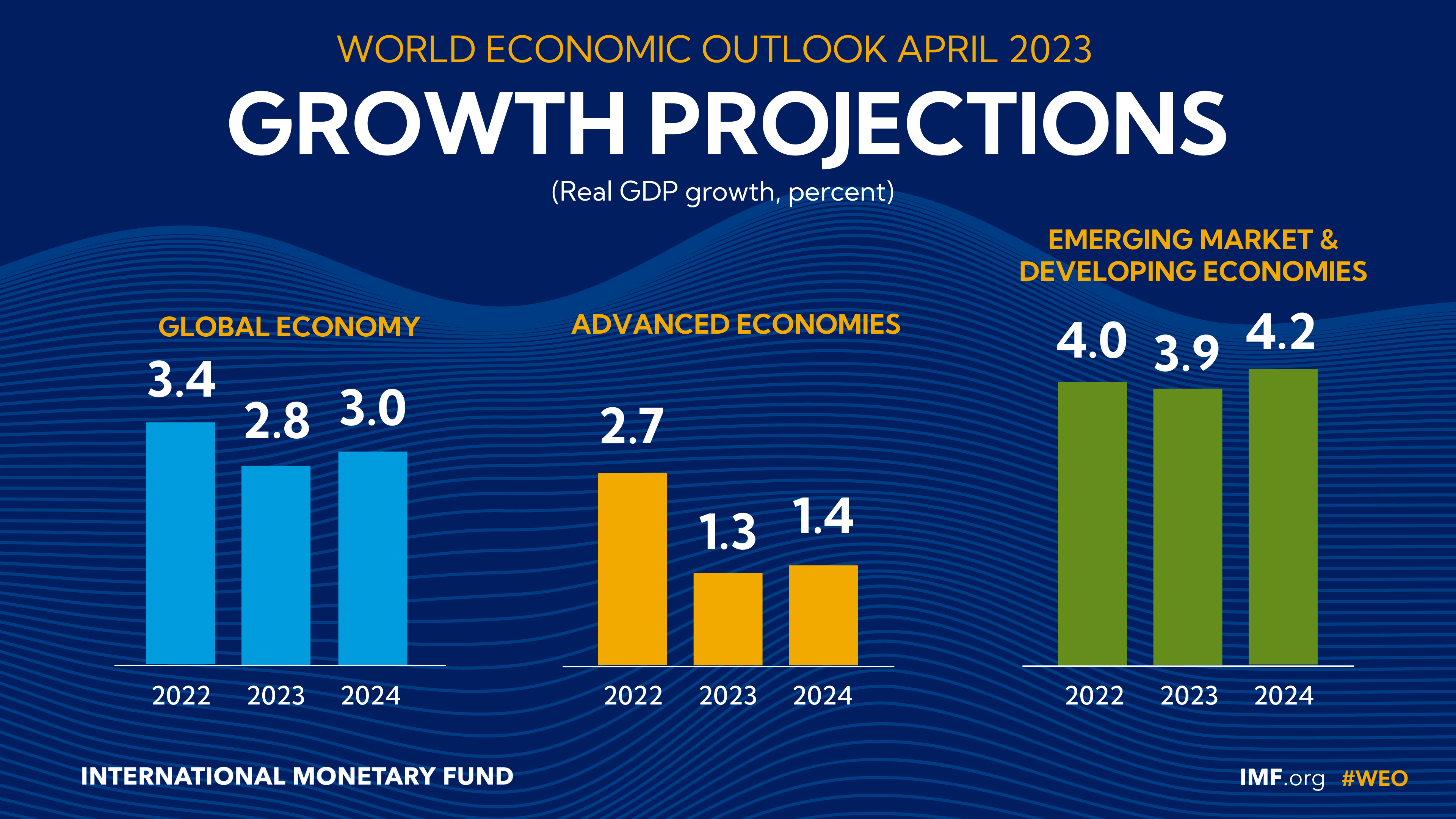
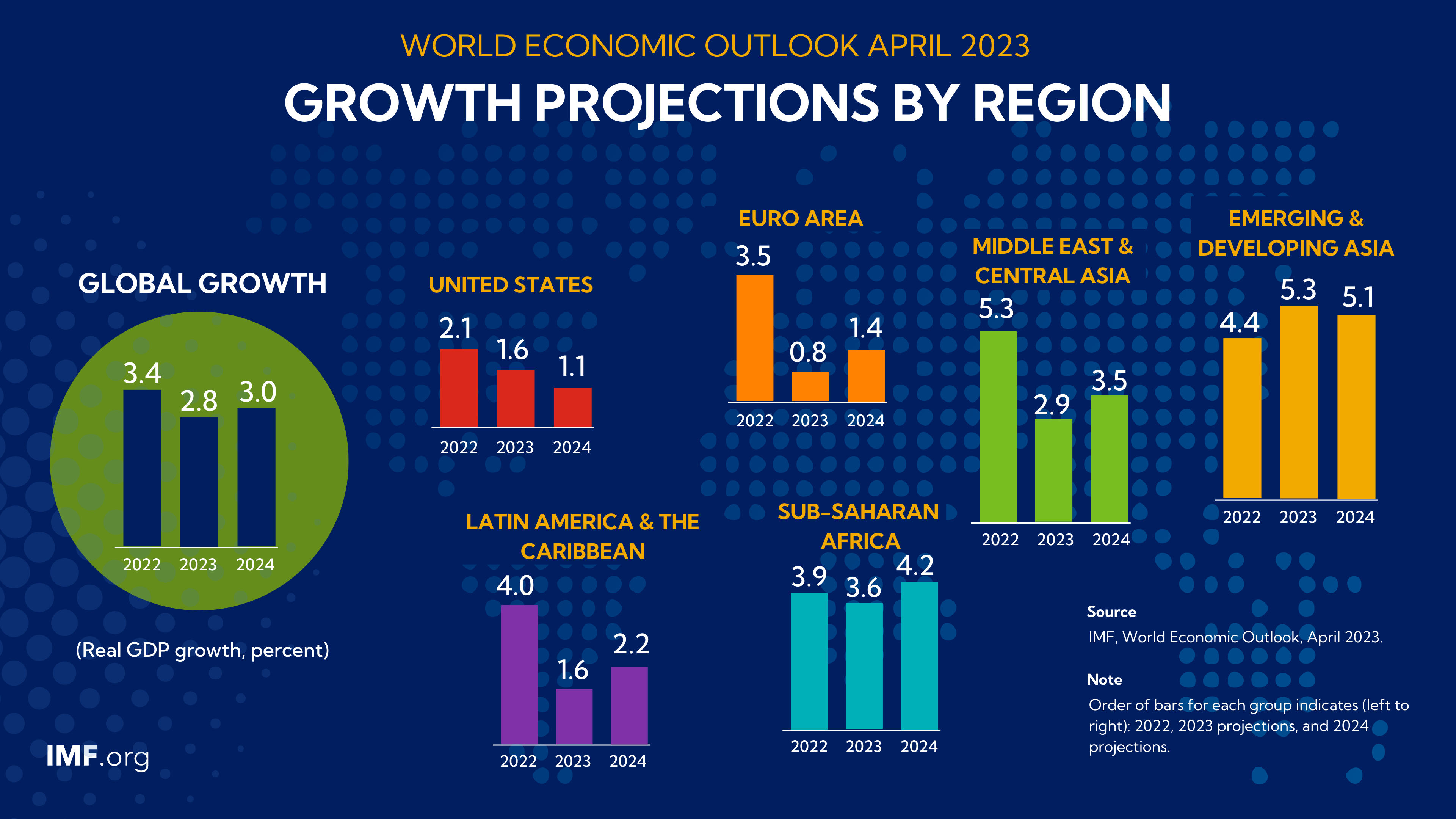
April 2023 by country and region
High Uncertainty
The global economic recovery continues, but many challenges keep arising. Inflation is slowly declining, but economic growth remains unprecedentedly low and financial risks have risen. The possibility of more or less accurate forecasting is extremely low, and the range between negative and positive scenarios is extremely wide.
Global Trade
The WTO currently forecasts growth by 1.7% in goods trade in 2023 (last October, the growth was expected to be by 1%). The prospects for the global economy have improved slightly, but the trade rate is still expected to be lower than in previous years.
Forecasts for 2024 show that trade and the GDP growth are returning to more normal ranges, with trade growth potentially rising to 3.2%, but it is better to remain cautious about these forecasts given many continuing uncertainties related to monetary policy, financial market volatility, and geopolitical tensions.
New risks that could negatively affect this forecast include vulnerabilities recently discovered in the banking sector. The effects of recent bank failures in the USA and Europe appear to have been largely contained, but a rapid rise in interest rates is bound to create tension in financial markets, which could affect trade.
However, there is some potential for optimism due to the alleviation of anti-Covid restrictions in China.